Introduction Fabric pilling, which happens from wear and friction, is a common issue affecting fabric…
Knowledge Share: 13 kinds of Spinning Processes
Different spinning process technologies have different effects on the physical properties and appearance of the yarn, and can even lead to different characteristics of the end product. In this article, we will systematically introduce 13 kinds of spinning processes and their respective characteristics and scope of application.
Table of Contents
Ring Spinning
The most versatile spinning method in the market today, where strips or roving are drawn and fibre strips are introduced through the ring spindle wire ring spinning, the tube winding speed is faster than the wire ring, and the cotton yarn is flicked to make a fine yarn.
Features & Applications
It is widely used in spinning project of various short fibres. The yarn has a compact structure and high strength, and is suitable for thread making as well as various products such as weaving and knitting.
Process
Clearing room – carding – pre-merge – strip and roll – combing – first merge – second merge – roving – spinning – winding
A more detailed and comprehensive guide of yarn spinning process in this post: Spinning Process Overview: From Fiber Material to Yarn
Twistless Spinning
This is a method of spinning in which the fibres in the whiskers are bonded to each other to form a yarn using a binder.
After the roving has been drawn by a drafting device, the fibre strips are conveyed to a twisting drum, where they come into contact with a thin layer of binder from a tank on the drum. The fibre strips are transported forward by several small rotating pressure rollers together with the drum, one of which also makes an axial reciprocating movement at the same time to roll the fibre strips into a round cross-section and to make each fibre come into uniform contact with the binder. The round fibre strips are dried by a heater and the fibres adhere to each other to form a yarn. The spinning speed can be 2 to 4 times greater than conventional spinning methods, and the yarn made can be used for weaving.
Features & Applications
Home textile products (pajamas, bed blankets, towels, towels, bath towels, shower caps, high-grade uniforms, baby suits, pillowcases, etc.) are characterised by their softness, puffiness, strong absorption of perspiration, and their wearing of cotton, warmth, lightness, translucency, and thinness.
Self-twisting Spinning
This is a kind of non-traditional spinning method.
Two fibre strips are drawn thin by the drafting device, and output from the front roller and twisting roller, and merge at the guide hook. The twisting rollers not only rotate, but also rapidly reciprocate axially to twist the yarn, so that the yarns before and after the twisting rollers are twisted in the opposite direction. The morphology of self-twisting yarn is characterised by the alternating positive and negative twisting of adjacent yarn segments, with no twisting at the alternating places. If you want to know more about yarn twisting, you can go ahead to this article: All about Yarn twisting.
Features & Applications
This spinning method is used exclusively for multi-stranded yarns, e.g. for woollen or imitation woollen synthetic fibre products. High-quality self-twisting yarns can be used directly for weft knitting, but for warp yarns for weaving, twisted self-twisting yarns must be used to improve the strength properties.
Pot spinning
This is a continuous spinning method that uses a high-speed centrifugal tank (cup) and a lifting guide tube to carry out twisting and winding. The roving is continuously output from the front roller after the drafting device, and enters the cylindrical centrifugal canister with high speed rotation through the yarn guide hook and yarn guide tube. The yarn sticks to the inner wall of the canister under the effect of centrifugal force and rotates with the canister, so that the yarn between the lower end of the yarn guide tube and the front roller is subjected to twisting, and the horizontal direction of the yarn under the yarn guide tube is lagging behind the centrifugal canister in the speed of rotation to produce coiling.
Guide tube according to a certain rule of lift, the formation of cross-winding yarn cake, winding to a certain length requirements, the front roller to stop the output of fibre strips, the guide tube rises out of the centrifugal canister, will be the empty tube to the centrifugal canister down sharply, the yarn head hooked on the lower part of the cylinder tube hook yarn, so that the yarn on the yarn cake back winding to the cylinder tube, back to the completion of the windings, take down the tube full.
Features & Applications
In comparison with ring spinning, power consumption, back to more silk, broken head difficult to deal with, yarn rewinding to the tube, the front roller needs to stop, affecting productivity, now few people use.
Cap Spinning
This is a spinning method in which the actual yarn is twisted and wound by means of a spindle cap and a tube. Commonly used in wool and linen spinning. The bellows type spindle cap is fixed on the top of the spindle and the tube is attached to the spindle. The roving is drawn thin by the drafting device and then the fibre strip is continuously output from the front roller, which is wound on the tube through the guide hook and the lower edge of the spindle cap. When the tube rotates, the yarn is driven to rotate around the spindle cap, and the yarn is continuously twisted back. The friction resistance of the spindle cap to the rotating yarn makes the yarn continuously winding on the tube. The tube is lifted and lowered with the lifting plate according to a certain law, and the yarn is wound into a certain form of winding.
Features & Applications
The spinning tension of the cap spinning method is small and the breakage is less.
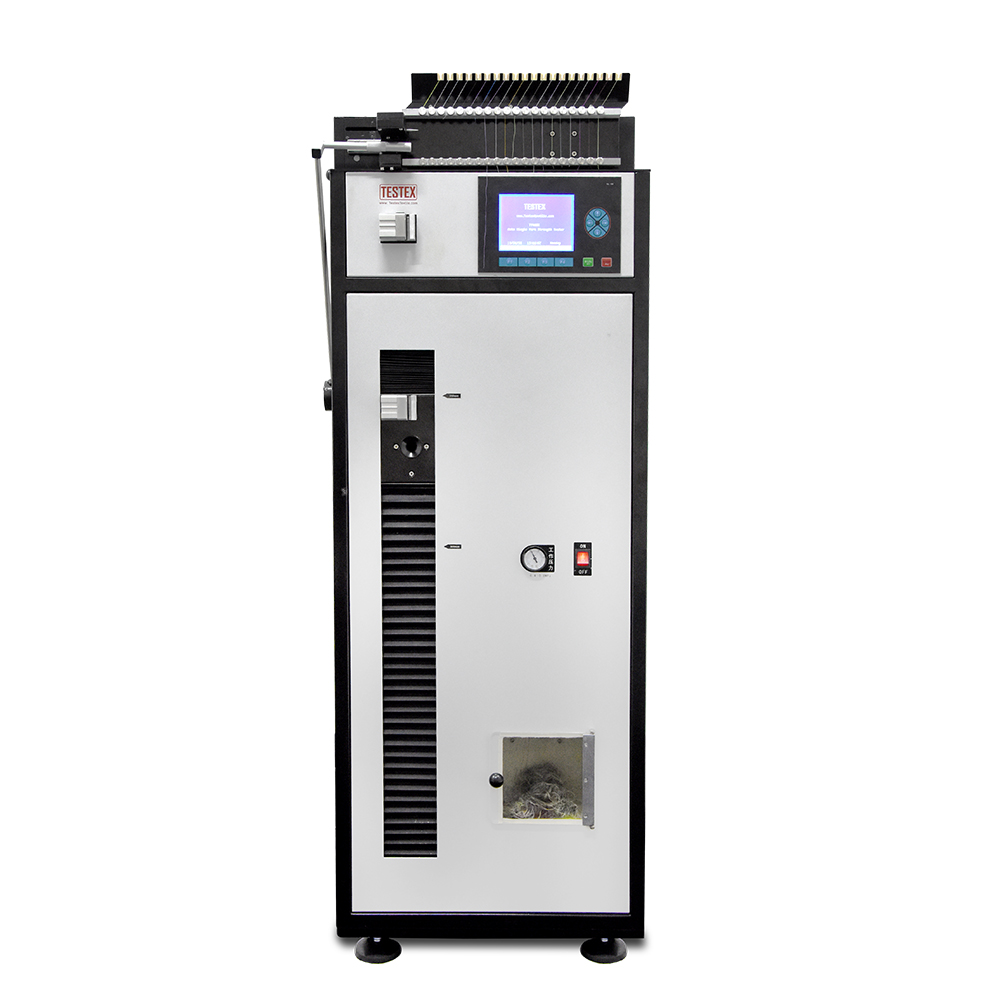
Automatic Single Yarn Strength Tester TY400C is used for testing the breaking strength and elongation at the break of single yarns of various cotton, wool, hemp, chemical fiber, pure spinning, corded spinning, and yarns. It can test the physical indexes such as breaking strength, breaking elongation, breaking strength, and breaking time of a single yarn.
Mule Spinning
A method of spinning in which the three roles of drafting, twisting and winding of the yarn are performed periodically.
A working cycle is divided into the following four stages:
Stage 1: Spinning out. The drafting device drafts the roving and sends out the fibre strips, the walking spindle carriage leaves the drafting device and moves outwards, slightly drafting the roving, the spindle rotates and twists the roving.
Stage 2: Flicking. The drafting device and the walking spindle car stops, the spindle rotates continuously to complete the twisting of the yarn.
Stage 3: Unwinding. Drawing device and walking spindle car continue to be stationary, the spindle to twist the opposite direction of the slow rotation, the yarn ring from the tip of the spindle back out of the winding, the upper forming hook down, to guide back out of the winding of the yarn ring, the lower forming hook up, pulling the yarn tight.
Stage 4: Winding. The drafting device continues to stop, the walking spindle car quickly moves towards the drafting device, the spindle rotates in the direction of twisting, and the yarn is wound up, the upper forming hook guides the yarn so that it is wound up tightly and formed into a certain roll, and the lower forming hook pulls the yarn tightly, which has been replaced by ring spinning and so on.
Wrap Reel, to produce skeins of yarn of a pre-determined length and number of turns for count and strength testing. Yarn Length Measuring Device complies with ISO 2060, ASTM D1907/2260, BS 2010, etc.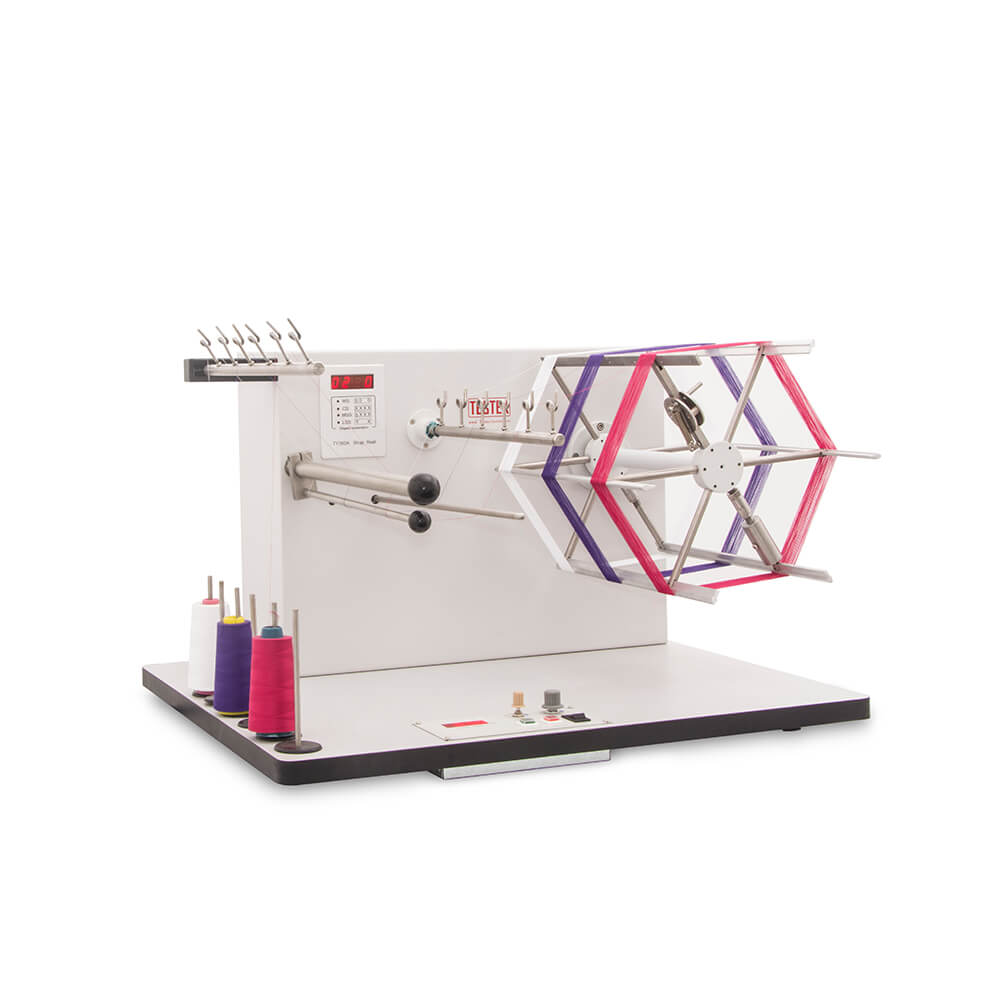
Break Spinning
This is a new spinning method that loosens fibre strips into single fibres and coalesces the single fibres into free-end fibre strips, which are then twisted into yarn. The coalesced fibre strips are rotated together with the yarn when twisting and are in free-end shape. Since the fed fibre strips and the free-end fibre strips are in a fractured state, it is also known as “Fracture Spinning”. There are different methods to coalesce the single fibres into free-end fibre strips, such as break spinning or rotor spinning, electrostatic spinning, vortex spinning and friction spinning, etc., of which the break spinning is the most common application. Nowadays, break spinning is mostly referred to open-end spinning.
Features & Applications
Break Spinning has the following features over conventional ring spinning:
- Twisting is separated from the winding motion. The total draft on an airflow-spinning machine is much larger than on a ring-spinning machine, and twisting can be carried out at high speed;
- After twisting, the yarn is directly wound into a cylinder, with a large winding capacity and a simplified process;
- Reduce the labour intensity of workers and improve the working environment.
OE-spinning(open end spinning)
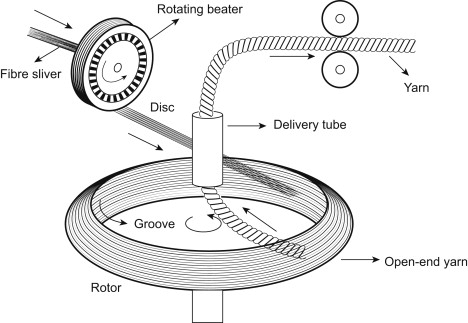
It is also known as “rotor spinning”, one of the most effective break spinning methods. The core is a spinning cup, the fibre strip from the feed rollers and the plate between the input, by the high speed of small rollers (combing rollers) open into a single fibre. Negative air pressure in the spinning cup makes the single fibre enter the spinning cup with the supplementary air flow through the conveying pipe. Under the action of centrifugal force in the cup of high-speed rotation, along the smooth inner wall of the rotating cup close to the largest inner diameter of the cohesive groove, the formation of a ring-shaped fibre head and joints, the lead yarn yarn tail with the supplemental airflow from the lead tube into the same due to the centrifugal action of the rotating cup attached to the cohesive groove, so that the yarn tail and fibre strip connection. When the lead yarn is pulled out of the spinning cup, the fibre strip leaves the cohesive groove with the yarn tail, and at the same time is twisted into yarn by the high rotation of the spinning cup, and is pulled out by the output roller through the twisting disc and the lead yarn tube, and then wound into a tube driven by the groove tube.
Features & Applications
It is suitable for spinning short fibre, medium and coarse special yarns, with clean and even fibre strips and more twisted yarns.
Its form is different from ring spinning, the appearance of airflow spinning is twisted, the core of the yarn is surrounded by a layer of low-twist fibres, from the core of the axis to the surface of the finished yarn, subjected to uneven distribution of tension.
The yarn of airflow spinning is mostly used for weaving corduroy, labour cloth, colour velvet and printing velvet.
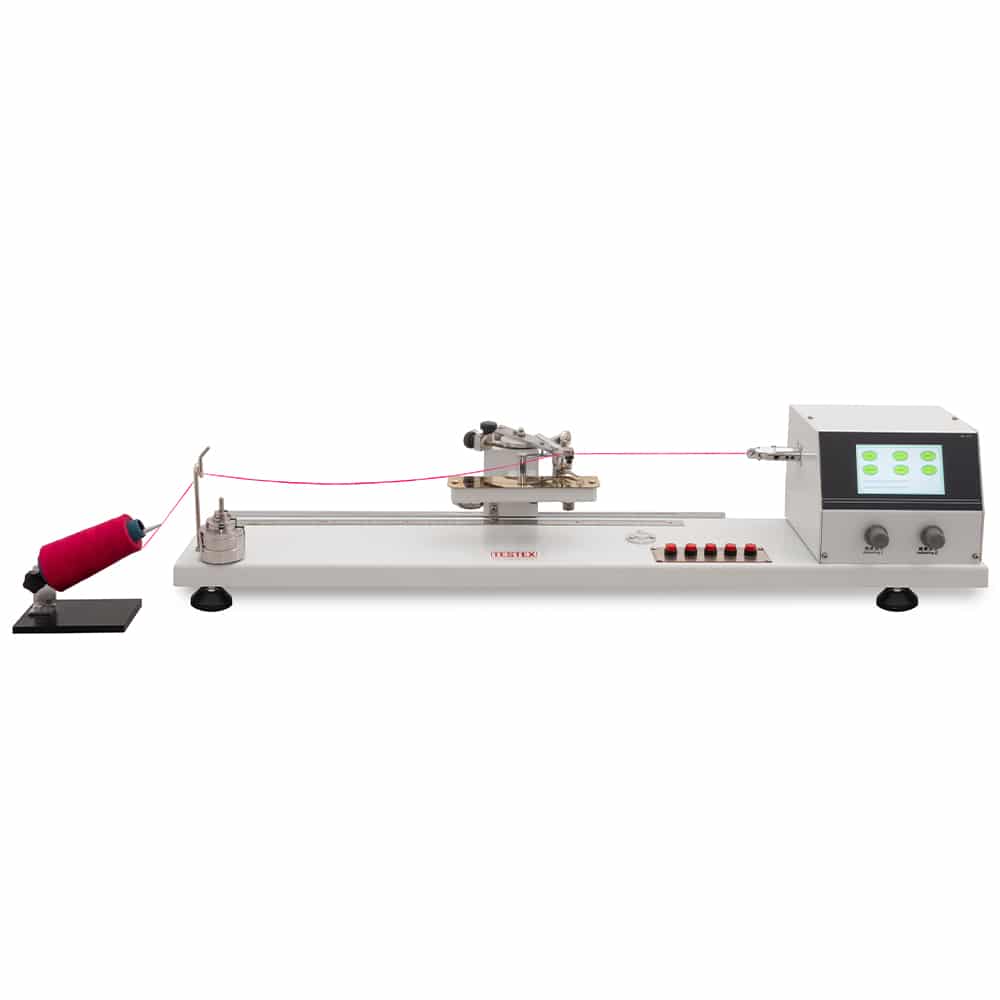
Yarn Twist Tester, is designed to determine yarn twists in single or plied yarns, quadrant type with auto stop & reverse for conventional or untwist/re-twist methods. Twist Tester Machine complies with ISO 2061, ASTM D1422/1423, BS 2085, etc.
Process
OE-spinning process: clearing – carding – the first merging – the second merging – OE-spinning
Electrostatic Spinning
It is one of the break spinning methods. It consists of the process of fibre opening, conveying, electrostatic coalescence, open end twisting and tube winding.
Among them, there are two methods of fibre opening and conveying:
(1) With roller drafting as the opening mechanism, fibre transport using electrostatic field action.
(2) to the prick roller as a loosening mechanism, the use of airflow conveying cotton fibres.
Features & Applications
Electrostatically spun yarn is suitable for weaving sheets, furniture cloth, knitted jacquard tablecloths and curtain fabrics and other products; spinning a variety of blended yarns, slub yarns and core yarns, but also can be made with cloth unique style of fabrics.
Vortex Spinning
One of the OE-spinning methods. The fibre strip is fed between the feed roller and the feed plate, and is loosened into fibres by the small high-speed rollers, and then enters the stationary vortex twisting tube tangentially with the air flow through the conveying pipe. The lower part of the vortex twisting tube is connected to the negative air pressure source, and the nozzle is tangentially configured with the inner wall of the twisting tube. The upward movement of the vortex part of the nozzle is weakened by the negative air pressure source in the lower part of the tube, so that the fibres entering the twisting tube tangentially are spiralled along the tube wall and coalesce into a rotating fibre ring in the stable vortex field. When the joints are made, the guide yarns follow the supplemental airflow through the guide tube, and are connected with the fibre ring under the effect of centrifugal force.
Features & Applications
The mechanism and operation are simple, the spinning speed is very high, no fibre dispersion and fewer flying flowers, and the twisting efficiency is low. It is suitable for spinning chemical fibre pure spinning or blended medium and coarse yarns, and it is used as pile yarn and core yarn with better effect.
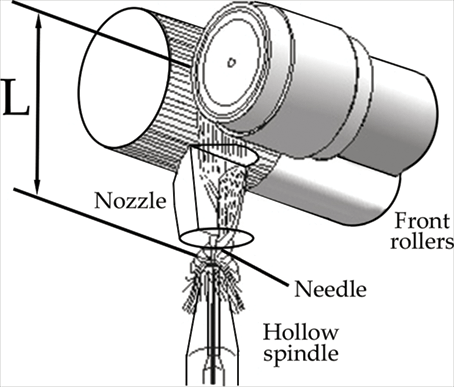 Air Jet Spinning
Air Jet Spinning
A non-traditional spinning method.
It uses jet airflow to spin yarns with some head-end free fibres wrapped around the periphery of the fibre strip after drafting and when the fibre strip is pretwisted. There are two types of nozzles: single nozzle and double nozzle type, the latter has good and stable spinning quality. The fibre strip is drawn thin by the drafting device, output from the front roller, through the first nozzle, the second nozzle, the guide hook, the guide rola, by the groove cylinder winding into a tube. The vortex of the two nozzles rotate in opposite directions, and the vortex strength of the second nozzle is greater than that of the first nozzle, so that the twisted yarn between the two nozzles can overcome the torque and resistance of the first nozzle added to the yarn, and pass to the front roller jaws. The free ends of the twisted fibres at the periphery of the fibre strand are influenced by the first nozzle and wrap around the fibre strand in the opposite direction. The twisted core portion of the fibres passes through the nozzle and is back-flicked, while the wrapped fibres are wrapped tighter and tighter in the reverse back-flick process.
Features & Applications
Compared with ring spinning, it has the advantages of high output, large rolls and short process. It is suitable for spinning all kinds of staple fibre and filament core yarn, and processing of medium-length chemical fibre yarn. Murata is the air-jet spinning expert, its products are MJS, MVS, RJS. air-jet spinning yarn shape like airflow spinning, hard feel, good hairiness.
Process
Air-jet spinning process: clearing room – carding – pre-merge – strip and roll – combing – the first merge – the second merge – air-jet spinning yarn
Friction Spinning
A method of yarn formation that utilises the friction of the machine surface against the yarn surface to produce a twist. The more established method is dust cage spinning.
Features & Applications
Unlike ring spinning, friction spinning does not require high-speed rotating parts to complete the task of twisting the yarn, and its main feature is the use of a screen with a suction device to twist the fibres into yarn. The main feature is that the fibres are twisted into yarn by means of a screen with a suction device. The screen is now mostly made in the form of a cylindrical dust cage and is therefore also known as dust cage spinning.
DREF spinning
A type of friction spinning, mostly collectively known as friction spinning, is a break spinning method.
The principle is that the fibre strip is loosened into a single fibre by the sash rollers, and is blown to the surface of a rotating dust cage by the action of the airflow, the spacing between a pair of dust cages is very small, and the rotating speed and steering are the same, the fibre layer rotating with the dust cage arrives at the triangular area of the two dust cages, and then it is twisted to become a yarn by the surface of the two dust cages and twisted into a yarn by the guiding hooks to lead the yarn to be pulled, and then it is directly wound to form a cylinder by the winding mechanism.
Features & Applications
Suitable for spinning coarse special yarns, can also be sandwiched filament spinning core yarn, usually woven thick fabrics or various blankets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between twistless yarn and twisted yarn fabrics?
Fibre arrangement
As the fibres in the yarn forming the fabric are arranged in parallel, the fibres have a large degree of freedom, so the fibres become ribbons or flattened after being squeezed, which makes it different from the fabrics formed by the traditional spinning method.
Appearance
Due to the reason that the yarns in the fabric are in ribbon cross-section, the coverage coefficient of the fabric is increased, so the fabric looks thick and compact, the fluffy feeling is good, and the fabric quality is lighter.
Processing
- No-twist yarn has no twisting, so the fabric shrinkage rate is smaller than that of traditional yarn fabrics, which can greatly save raw materials;
- The dyeing performance of twisted yarn fabrics is good, and it can get a mercerised effect.
- Twisted yarn fibres are exposed, and can be in full contact with the dyes, so the dyes are easy to dye twisted yarns are often mercerised, so that the fibres are aligned more neatly in order to obtain a good luster, while twisted yarns do not need this treatment;
- The fluffy effect of twisted yarn fabrics can be utilised to produce lighter, thicker and more comfortable fabrics.
What is the difference between soft twisted and zero-twist yarns?
Zero-twist yarn: to make the centre of the fibre hollow. Weakly twisted yarn is a deformed yarn made by twisting two yarns together and winding them separately after heat setting.
Soft twisted: cotton fibre and water-soluble polyvinyl chloride are spun into yarns, combined and twisted into threads, which can make towel fabrics achieve high softness and high water absorbency after being de-dimensioned in the finishing of fabrics. Soft twist is 10CM yarn with less twisting back (spinning), zero-twist is no twisting back, twisting the yarn is a means to improve the fastness of the yarn, but it will reduce the comfort, water absorbency and air permeability of the yarn. In terms of comfort, untwisted towels are better than weakly twisted towels, but their durability is not as good as weakly twisted towels.
In durability:
- Zero-twist yarn: no-twist yarn has lower durability than weak-twist yarn;
- Soft twisted yarns: weakly twisted yarns are more durable than weakly twisted yarns and less durable than face yarns.
In twist:
- Zero-twist yarns: no twist;
- Soft twisted yarns: weakly twisted yarns do not complete the twist of the cotton yarn when spinning, and generally only complete about 70% of the twist of the cotton yarn.
In terms of advantages and disadvantages:
- Zero-twist yarn: no-twist yarn fabric feel super soft and thick, but in the process of use, there will be some hair loss, which is caused by the process is difficult to eliminate the shortcomings, you can use warm water to wash again before use, you can remove the floating hairs, it can be very good to improve the phenomenon of hair loss;
- Soft twisted yarn: it will not be obviously hardened by repeated exposure to water, and the most crucial thing is that the production process will not produce additional environmental pollution.
The above is the detailed sharing towards different kinds of yarn-spinning processes. Want to stay on track with more professional and comprehensive textile testing knowledge? Please subscribe to us who will timely updates!








This Post Has 0 Comments